Linear Model Cheating Sheet
Linear Regression
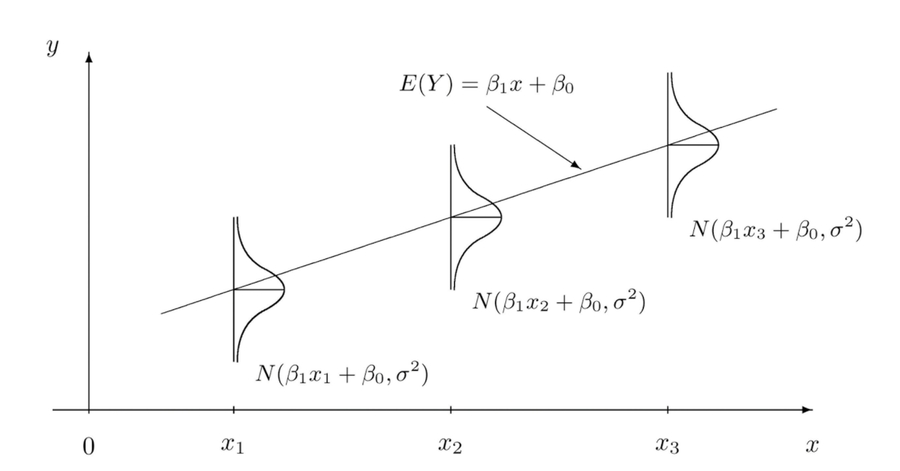
Definition
Representation
How to determine this model?loss function?
How is the performance of this model?
How can we compare this model with others model?
Multilinear Regression
Logistic Regression
图形/值域的理解
How to determine this model?loss function?
How is the performance of this model?
How can we compare this model with others model?
Compare with linear regression
Multiple Logistic Regression
Regularization——Ridge regression/Lasso regression
SVM
Last updated