A/B testing
What is the role A/B testing?
Controlled experiment(说白了就是控制control)
Compare one element(control) with itself with variations
Splits traffic 50/50 between a control and a variation
A nickname for a variety of testing that involves single element changes across multiple variations(说白了就是从顾客帮你做决定)
it could be A/B/C/D testing
A decision-making procedure(就是做个决定,蓝色还是绿色)
容易混淆
Customer-driven Development
Blue green deployment
FDA drug's effective test
Why/When do we use AB testing?
We are poor at assessing the value of our ideas
Solve visitor pain points
Get better ROI
Make low-risk modifications
Achieve statistically significant improvements
Profitably redesign
Improved Content Engagement
Reduced Bounce Rates, Increased Conversion Rates
Understand your customer
Higher Values
Ease of Analysis
Product iteration process, how to apply it?
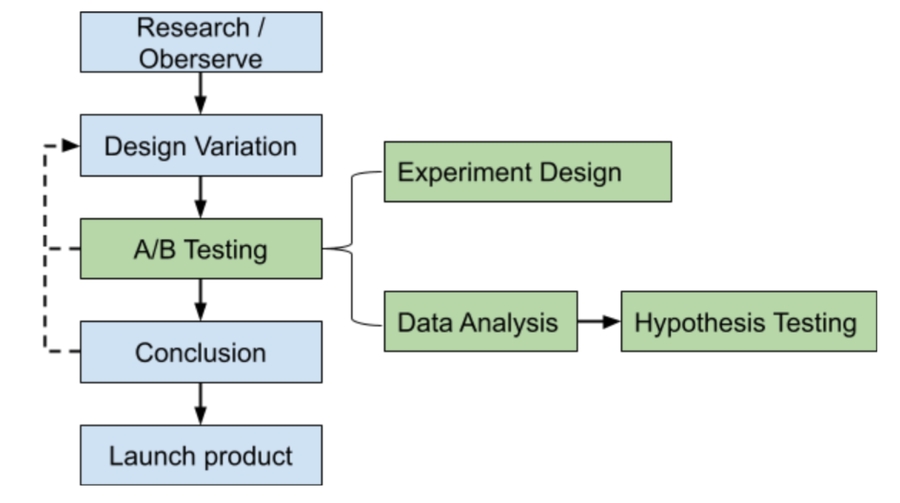
Research and observe
Research the behavior of the users and understand where they tend to bounce off the path leading to the goal. Then identify the problem: for example 'The signup form has too many fields leading to a high abandonment rate'
A/B Testing
To determine whether the new variation is doing statistically better (in term of certain metrics) (可能收获上去,评价下去)than the current version, using a randomized experiment.(这个其实就是A/B testing)
If it is, then we should replace the old version with the new one and expect to have better performance in the long run.(我们永远目标是long run)
Experiment design:
After developing a variation, then split the traffic 50/50 between the original and the shorter variation, and wait for the experiment to run until it has achieved statistical confidence(95% confidence is the accepted standard and your chosen software should report this. (后面还有个流程图)
Data Analysis
Conclusion: If the variation performs better, you implement it for all users. If it performs worse, you learn that form length is probably not responsible for the high abandonment rate and go back to identifying the problem
Launch
Decide whether we should launch the new product variation, or refine the design, based on the A/B testing results.
How to design A/B testing?
更科学的描述?What exactly is A/B testing doing?/When is A/B testing a good idea?
business角度:影响大,选择难
experiment角度:存在明显对照组/实验组;有适合的metric
test角度:在大范围可以有测试(功能/内容/外观/页面加载时间)
其他:
app/web page广告投放/算法和优化(推荐算法&产品优化)
Metrics
What is metrics?
Quantitative measurements that help you to gain insights(必须是数字化,比如说百分比点到第二页)
Assessing your product performance
Key performance indicator(KPI) -(就是和你的产品直接挂钩的最重要的matrics,不一定一定要赚钱)(选错matric可能把整个负责product拖下水)
Product KPIs can be related to user requirement, size, quality, product growth, or user comfort. or evaluate architectural measures, quality measures, software caomplexity, of functional size.
Which metrics is the better one?
direct/compound metric
high-level(unified)/low-level metric
Primary metrics/second metrics
常用metrics:有什么指标可以直接用呢?(你要注意当时公司在干什么!!!!!!)
customer retention
repurchase rate
daily active users(DAU)
feature usage这个feature有多少人用
user churn 流失
net promoter score用户对这个的口碑(比如说tesla车主,)
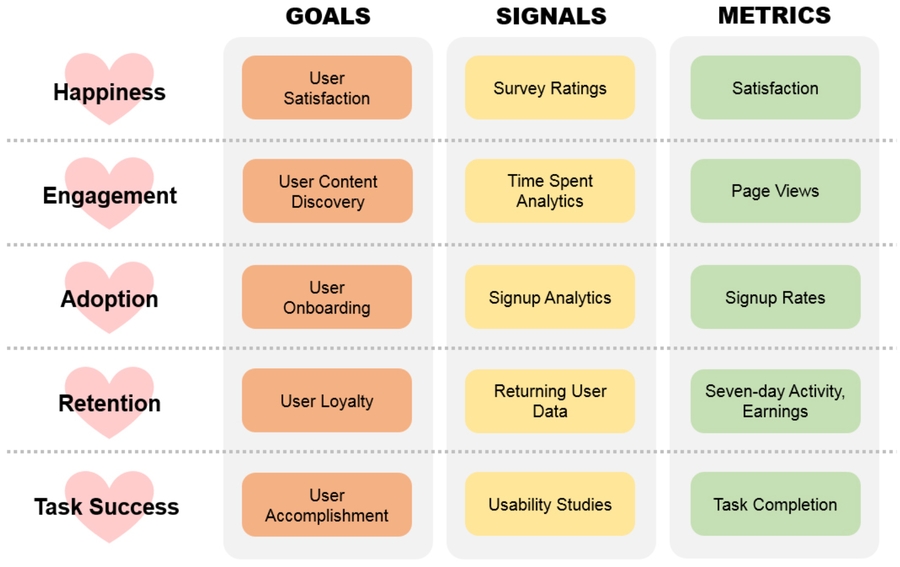
methodology(海盗&心模型)
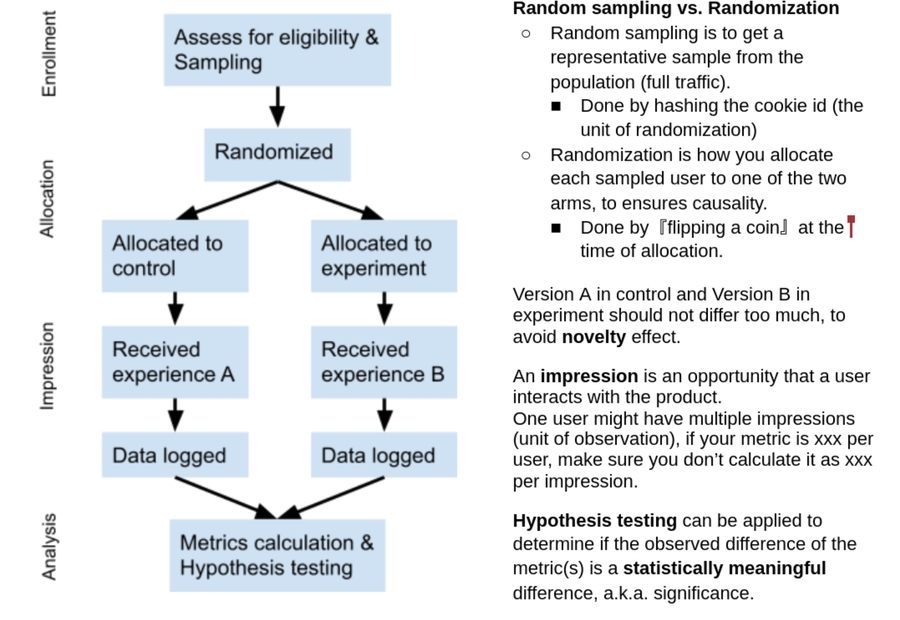
Random Experiment
(随机分配到不同组)In randomized experiments, users are randomly allocated to two different groups(experiment vs control). where the experiment group has a treatment(new design or feature) that the control does not (control has the current design)
(随机分配independent/distibution)Randomization makes the allocation independent of the potential outcome and makes the users in the experiment group and those in the control group identical in distribution
Therefore the mean difference in metric can only be attributed to the treatment
What can we go wrong?
Picking the Wrong metrics
Making Your Sample Size Too Small
Testing too many elements together
Gettting Tricked by Statistics
Not Questioning Your Results
Data biased(身份证的单双号)
Novelty effect
Not sure how to interpret results
More on experiment design
Match
一个现象能不能造成严重的影响,这个不是a/b testing,目标不是要选择
Typically used in observational studies(not randomized), but you can still use it in randomized experiments to reduce potential bias.
Matching is done by(这个如何matching?找背景一样呗)
Types of matching
Individual matching: one-to -one match on selected factors
Frequency matching: set-to -set match on the frequency of selected factors(比如说20-30男,相似的性质)
Propensity score matching: one-to-one matching on estiamted propensity score(PS) (比如说倾向性得分的&和set to set有类似的)
PS is the probability of getting selected in the experiment group(in step 1)
PS can be estimated by any classification model, typically logistic regression
Caveats
Segmentation
Post-randomization. Divide the users into subsets and do analysis per segment
Serves two purposes
If you suspect the effect may vary across different subsets of users(e.g. male prefers the green button, femal prefers the red button), segmentation helps your verify such heterogeneity(你已经上线产品,然后你发现了问题,像是组间差异)(看我和用户上的一些差别?)
If you suspect your randomization is not perfect(some confounding factors are imbalanced across two arms), segment-then-unify is an alternative to matching(可能正好是疫情期间)
Advanced control group settings
Holdout group(因为广告看了很久可能已经影响了,所以留了些彻底没有动过的人,彻底没有看广告的人)
Double control group(also called AAB test) -
Hypothesis Test
Why?
我们没有办法穷尽所有的数据,只能从整体中取出部分,通过研究部分来推测整体
In general, we do not know the true value of population parameters - they must be estimated. However, we do have hypotheses about what the true values are
The major purpose of hypothesis testing is to choose between two competing hypotheses about the value of a population parameter.
For example, one hypothesis might claim that the wates of men and women are equal, whil the alternative might clain that men make more than women
Definition?
Hypothesis testing is the procedure to determine if the estimated difference/relation is a statistically meaningful difference/relation
we can use the hypothesis testing tool to determine if the observed difference is statistically significant/meaningful.
(学术定义):用于判断,基于小样本数据的参数估计结论,今后能否在总体中长期保持。
(普通定义): 用于回答,产生这样的数据差异,到底是偶然还是必然?
The Logic of Hypothesis Testing
Null and alternative hypotheses(H0 and H1):建立原假设H0 以及备择假设H1
Calculate P-value and interpretation:选择合适的检测方法,计算p值
P< 0.05 decline(reject) H0, accept H1:当p值小于0.05时,拒绝原假设,病接受备选假设
Significance level
Key concepts
Hypothesis:
A specific claim about the population often described using an expression of the parameters
Null hypothesis :
The claim reflects the default situation, usually, it means no relation or no difference.(你做试验是为了证明有罪,虽然这里是无罪)
Alternative hypothesis :
The claim about the population when the null hypothesis is false. (parameter of interest )
P-value:
The probability of obtaining as or more extreme result than the current observation under the null hypothesis.
这个是不止是那个边界点,甚至大于边界点的都该如此
Significance level
The probability of rejecting when is true: must be pre-defined.(说白了就是你不想要的概率,所以不是推翻,而是概率很小,但是也不是说你的可以被接受,而是没办法拒绝,这个值很小)
Type I error:
This happens when is true, but is rejected.(冤狱)
Significance level = type I error rate = .
Type II error :
This happens when is true, but is not rejected.(漏网)
Type II error rate :
Power and :
the probability of rejecting , when is true. power = (火眼金睛)
Significance level = Type I error?
The trade of Type I error and Type II error?
Advance thinking:
如果你减少,很自然你会调整你的confidence interval。
CLT
原来分布最后趋向与正太分布.。只要你原来是独立同分布
Hypothesis Testing as an Algorithm
A/B testing(randomized experiment)中的假设检验
Metric以均值(sample mean, average)得形式定义
CTR(click-thru rate), DAU(daily active user), ARPU(annual revenue per user)
Think about Hypothesis Testing as an algorithm, such that it takes the data , ,and as input arguments, and returns the decision of rejecting or not
Practice
p-value/score
Sample size calculation
Statistical significance?
is the likelihood that the difference in success metric between a given variation and the baseline is not due to random chance
Common statistical significance level is 5%(, confidence level). You can use a different level depending on the actual test.
Two key variables to determining statistical significance: sample size and effect size.
How to determine sample size?
Higher confidence level requires larger sample size
Smaller effect size requires larger sample size
Sample size calculator
Test for Independence
What is this question?
How do we test if two random variables are independent?
How do we estimate the strength of dependence between two random variables?
How?
: Z is independent of Y:
: Z is not independent of Y
Pearson's Chi square test statistic for independence is
where
Under the null hypothesis, . Thus, a significance level test is obtained by rejecting the null hypothesis where
Two binary Variables
Simpson paradox
Two continuous variables
One continuous variable and one discrete
Statistic Module Review
Summary
Your team suggests a new way to boost revenue by adding a new product category on your site but management is worried that might actually hurt sales and turn away existing vendors. What do you do?
你先搞清楚他要什么,procedure,test?怎么入手,怎么解决,解决到什么地位?
第一个步骤:说白了就是一片迷茫,先quantative,就是先找一个metrics,取一个好的matric(海盗模型,heart模型找到metric);找到metric只是on the same page
第二个步骤:就是根据这个metric,来看看这个好不好,有没有用?那就是hypothesis
第三个步骤:你的testing里面的细节
第四个步骤:虽然如此好,但是会不会出现问题?(probability,或者有一定概率会错)
What is your first step?
How shall we do randomization? What are we going to randomize?
What is the sample size?
Data collection
Perform hypothesis testing
What if the hypothesis can not be rejected?
What if we have conflicting metrics results?
What if the hypothesis is rejected?(type I error?)
Common statistical concerns in A/B testing
Misinterpretation of p-value
Causation vs association
Missing data
Multiplicity
Subgroup analysis
A/B testing pipeline 1
Objective define
Metrics and effects define
Experiment setup
Conduct hypothesis
Result Interpretation
Last updated